- actor: 对应 policy update
- critic: 对应 policy evaluation 或者 value evaluation
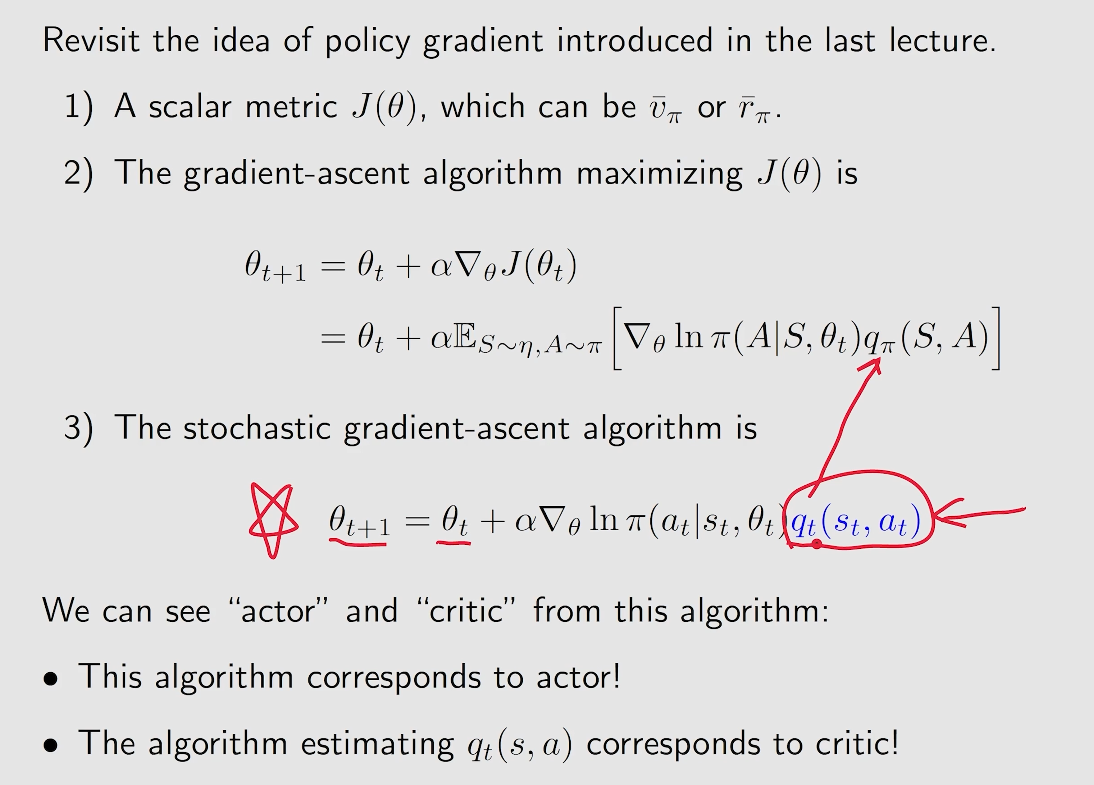
显然,是在基于 策略梯度上升 算法的基础上,将对于 Q 值的估计通过一个网络来进行描述,这个便成为 critic, 而对应的策略梯度上升算法就是对应 actor。

显然,是在基于 策略梯度上升 算法的基础上,将对于 Q 值的估计通过一个网络来进行描述,这个便成为 critic, 而对应的策略梯度上升算法就是对应 actor。
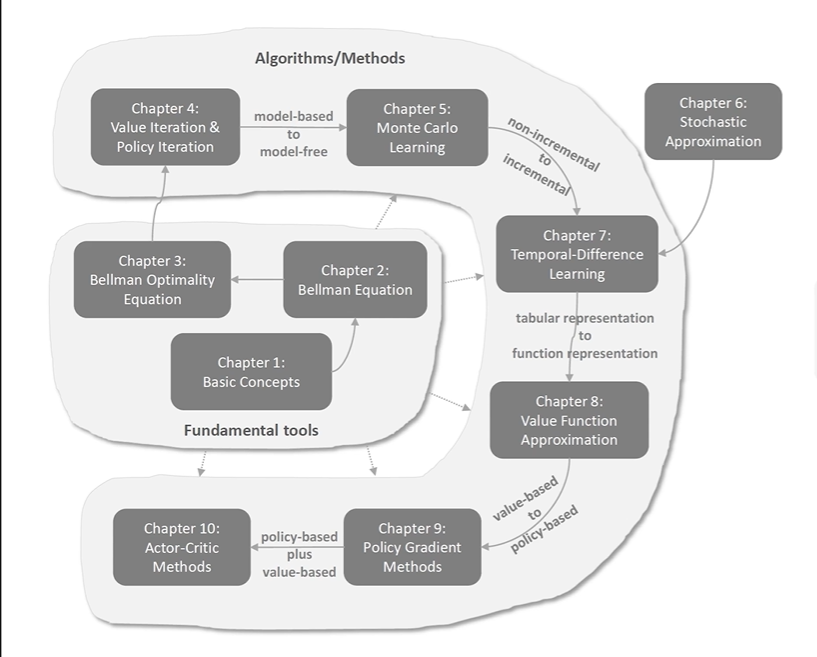
将基于表格表示的策略 转换为 基于函数表示的策略。
即此时策略 π 可以描述为:
对于 q-value 的估计从 基于表格的 (tabular representation) 转换到 基于函数的 (function representation)
考虑一个复杂的均值估计问题: 计算
ω=E[R+γv(X)],
针对 mean estimation 问题进行研究,因为在 RL 中 无论是 state value 还是 action value 其定义都是一个均值 (means)
Stochastic approximation(SA): SA refers to a broad class of stochastic iterative algorithms soloving root finding or optimization problems.
如何在没有模型 (即p(r∣s,a),p(s′∣s,a)等均未知) 的情况下进行估计
通过 Monte Carlo estimation.
其核心思想是:
若有一系列(i.i.d)样本采样,得到一个样本序列x1,x2,…,xN
那么对于随机变量X的估计可以为:
E[x]≈xˉ=N1j=1∑Nxj
该方法成立的数学依据是 大数定理 (Law of Large Numbers)
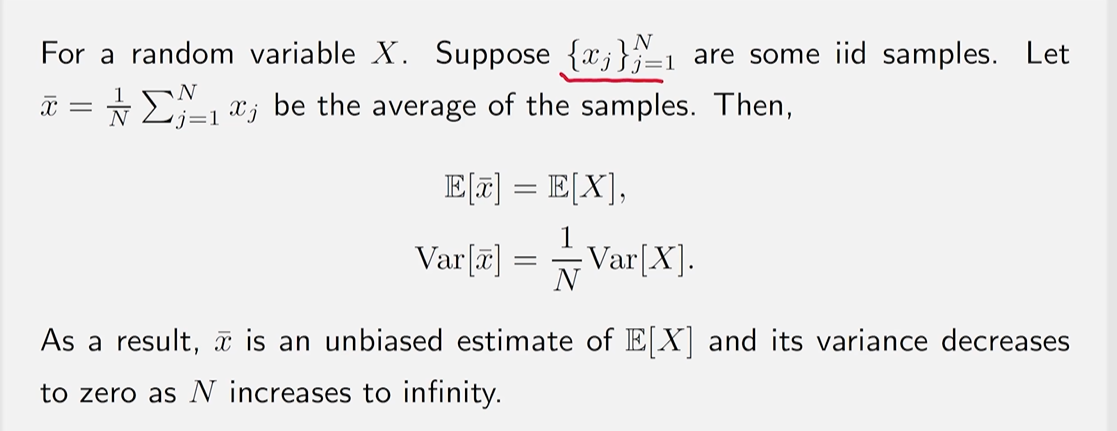
样本必须是独立同分布(iid, independent and identically distributed)
为什么考虑 mean estimation. 因为无论是 state value 还是 action value 其原始定义都是从期望出发的。
vπ(s)=E[Gt∣St=s];qπ(s,a)=E[Gt∣St=s,At=a]
贝尔曼最优公式:
v=f(v)=πmax(rπ+γPπv)
最优策略的定义:
A policy π∗ is optimal if π∗(s)≥vπ(s) for all s and for any other policy π.
需要确定几件事:
State(状态):The status of the agent with respect to the environment.
State Space(状态空间): 所有状态的集合。S={si}i=1n。
Action(动作): 对于每一个状态,都有可选择的动作。
Action space of a state: 对应状态中所有可选择的动作集合。A(si)={ai}i=1n
State transition(状态转换): s1→a1s2。定义了agent与环境的交互行为。
State transition probability: p(s2∣s1,a1),即状态s1采用动作a1转到状态s2的概率。
Policy π: 指导agent在当前状态下选择哪个动作。
Reward(奖励): 在执行一个动作后获得的一个常数(依赖于当前状态和所采取的动作)。同样可以用条件概率的形式进行描述,如p(r=1∣s1,a1),即在状态s1下采用动作a1获得的奖励r=1的概率。
Trajectory:a state-action-reward chain.(可以有限,也可以是无限长的trajectory)
s1r=0→a2s2r=0→a2s5r=0→a2s8r=1→a2s9.
个人理解,trajectory是在策略给定下,agent可能走出的全部轨迹,并非只是一个单一的轨迹。
Return of a trajectory:将对应的轨迹所获得的所有reward的总和,可以粗步衡量一个策略的好坏。
Discounted return(of a trajectory):为了应对具有无限步的trajectory的return=∞的情况。 s1r=0→a2s2r=0→a2s5r=0→a2s8r=1→a2s9r=1→a2s9r=1→a2s9…. 此时该trajectory的return=0+0+0+1+1+⋯=∞。 引入discount rate, γ∈[0,1). 此时对应的discounted rate=0+γ0+γ20+γ31+γ41+⋯=γ31−γ1 显然,如果γ接近0,即此时的discounted return越短视,注重近期的reward;γ接近1,更远视,更注重长远的reward。
Episode(trial):When interacting with the environment following a policy, the agent may stop at some terminal states. The resulting trajectory is called an episode(or a trial)/ 即表示具有终止状态terminal states的trajectory,通常是具有有限步长的trajectory. 同理,这样的任务称为episodic tasks。
continuing tasks:即不具备terminal states的任务,会与环境一直交互下去。 可以通过设置将episodic tasks转换成continuing tasks,如可以在target states中限制action space,控制其一直待在target states中。 Deterministic — Stochastic